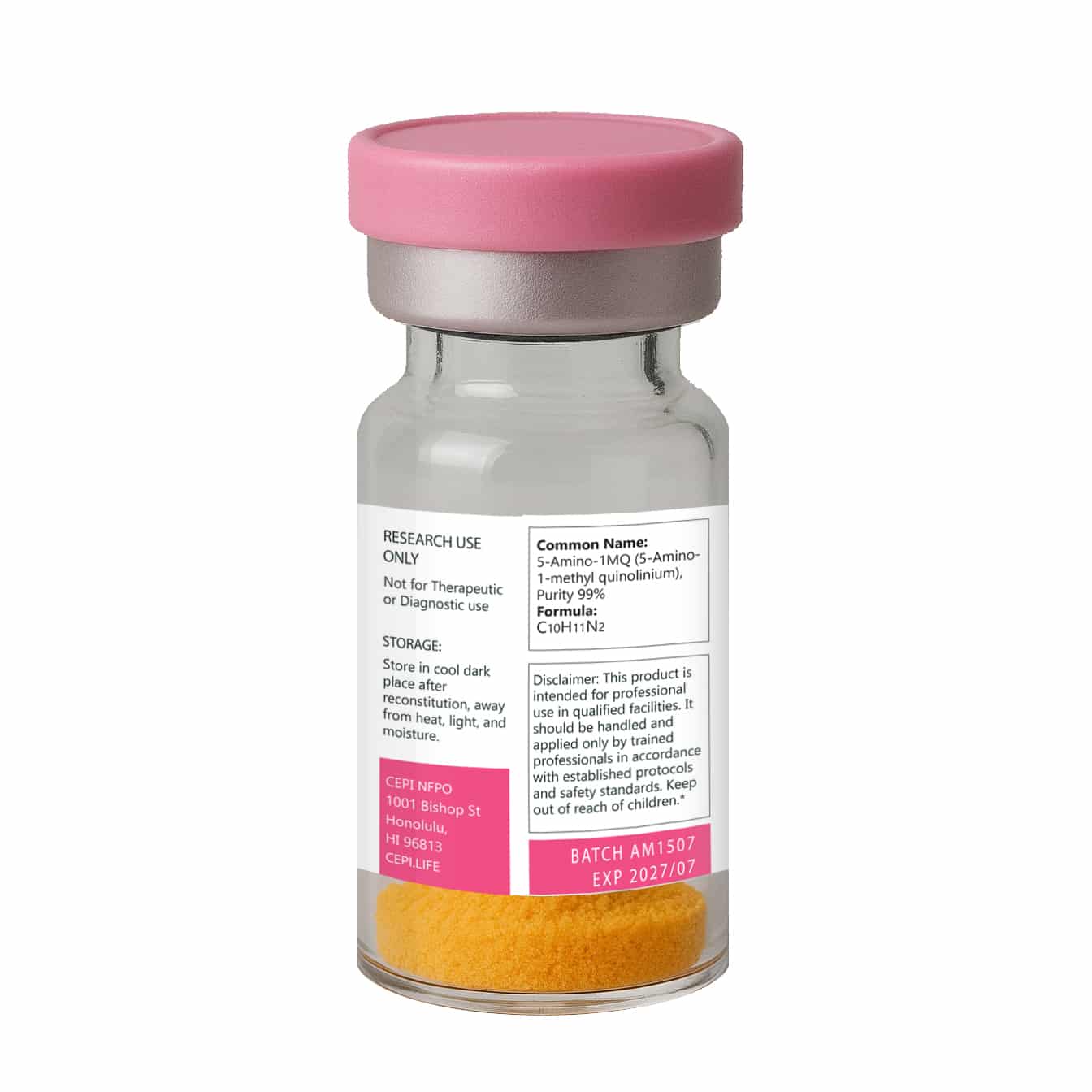
5 Amino – 1MQ 50 mg
High-Purity Research Peptide – NNMT Inhibitor
5-Amino-1MQ (5-Amino-1-methylquinolinium) is a synthetic compound recognized for its selective inhibition of the enzyme nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT). By blocking NNMT, this molecule shifts key cellular pathways that regulate NAD+ metabolism, energy balance, and fat storage in experimental models.
$75.00
Key Research Highlights:
-
Metabolic Studies: Shown to increase NAD+ availability, support mitochondrial function, and influence lipid metabolism in preclinical settings.
-
Obesity & Weight Research: Animal studies report reduced fat mass and improved metabolic health without changes in food intake.
-
Cellular Longevity: Linked to mechanisms involving DNA repair, epigenetic remodeling, and redox balance.
-
Oncology Applications: Early research suggests potential in cancer models via effects on histone methylation and tumor microenvironment modulation.
Specifications:
-
Molecular Formula: C10H11N2
-
Molecular Weight: 159.21 g/mol
-
Synonyms: 5-amino-1-methylquinolinium
Storage & Handling:
Supplied as a lyophilized powder for extended stability and integrity. No fillers added.
⚠️ For Research Use Only. Not intended for human consumption. This compound is provided strictly for laboratory and in vitro research by qualified professionals.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
5-Amino-1MQ Research
5-Amino-1-methylquinolinium (5-Amino-1MQ) is a synthetic small molecule in the methylquinolinium family, defined by a quinolinium backbone with an amino group at the 5-position and a methyl group at the 1-position.
Its primary scientific interest comes from being a potent and selective inhibitor of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT)—an enzyme involved in critical pathways linking metabolism, redox balance, and oncogenesis.
Mechanisms of Action
By inhibiting NNMT, 5-Amino-1MQ directly influences NAD+ metabolism, histone methylation, and downstream gene expression. NNMT normally consumes nicotinamide, reducing intracellular NAD+—a vital cofactor in DNA repair, energy production, and transcriptional control.
-
Preclinical adipocyte studies show that 5-Amino-1MQ raises NAD+ levels by 1.2–1.6× compared to controls, underscoring its impact on metabolic homeostasis and cellular health.
-
Epigenetic effects include altered histone methylation patterns, reshaping gene programs linked to metabolism and cancer progression.
Metabolic and Anti-Obesity Potential
Research highlights 5-Amino-1MQ as a promising metabolic modulator:
-
In diet-induced obesity mouse models, treatment significantly reduced body weight, adipose tissue mass, and adipocyte size.
-
Importantly, these benefits occurred without changes in food intake, suggesting its action comes from suppressing lipogenesis (fat creation) rather than appetite suppression.
Such findings position 5-Amino-1MQ as a candidate compound for further exploration in obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes.
Applications in Cancer Research
Beyond metabolic health, 5-Amino-1MQ shows compelling potential in oncology:
-
Epigenetic remodeling: Alters histone methylation in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), disrupting tumor-supportive signaling.
-
Tumor microenvironment effects: Reduces tumor cell proliferation and modifies surrounding tissue dynamics in animal models.
These dual actions suggest possible roles for 5-Amino-1MQ in monotherapy and combination strategies, particularly in gynecological and other malignancies.
Pharmacology Insights
Early data confirms cellular permeability and bioactivity, supporting research across multiple tissue types. Ongoing studies aim to refine its pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics—focusing on metabolic stability, targeted delivery, and minimizing off-target effects.
References:
-
Conlon, N., & Ford, D. (2022). A systems-approach to NAD+ restoration. Biochem Pharmacol.
-
Myong, S., Nguyen, A., & Challa, S. (2024). NAD+ metabolism in gynecological cancers. Cancers.
-
Li, X., et al. (2022). NNMT as a biomarker and therapeutic target in cancer. Front Oncol.
-
Liu, J., et al. (2021). NNMT in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Biomed Res Int.
5-Amino-1MQ Research
5-Amino-1-methylquinolinium (5-Amino-1MQ) is a synthetic small molecule in the methylquinolinium family, defined by a quinolinium backbone with an amino group at the 5-position and a methyl group at the 1-position.
Its primary scientific interest comes from being a potent and selective inhibitor of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT)—an enzyme involved in critical pathways linking metabolism, redox balance, and oncogenesis.
Mechanisms of Action
By inhibiting NNMT, 5-Amino-1MQ directly influences NAD+ metabolism, histone methylation, and downstream gene expression. NNMT normally consumes nicotinamide, reducing intracellular NAD+—a vital cofactor in DNA repair, energy production, and transcriptional control.
-
Preclinical adipocyte studies show that 5-Amino-1MQ raises NAD+ levels by 1.2–1.6× compared to controls, underscoring its impact on metabolic homeostasis and cellular health.
-
Epigenetic effects include altered histone methylation patterns, reshaping gene programs linked to metabolism and cancer progression.
Metabolic and Anti-Obesity Potential
Research highlights 5-Amino-1MQ as a promising metabolic modulator:
-
In diet-induced obesity mouse models, treatment significantly reduced body weight, adipose tissue mass, and adipocyte size.
-
Importantly, these benefits occurred without changes in food intake, suggesting its action comes from suppressing lipogenesis (fat creation) rather than appetite suppression.
Such findings position 5-Amino-1MQ as a candidate compound for further exploration in obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes.
Applications in Cancer Research
Beyond metabolic health, 5-Amino-1MQ shows compelling potential in oncology:
-
Epigenetic remodeling: Alters histone methylation in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), disrupting tumor-supportive signaling.
-
Tumor microenvironment effects: Reduces tumor cell proliferation and modifies surrounding tissue dynamics in animal models.
These dual actions suggest possible roles for 5-Amino-1MQ in monotherapy and combination strategies, particularly in gynecological and other malignancies.
Pharmacology Insights
Early data confirms cellular permeability and bioactivity, supporting research across multiple tissue types. Ongoing studies aim to refine its pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics—focusing on metabolic stability, targeted delivery, and minimizing off-target effects.
References:
-
Conlon, N., & Ford, D. (2022). A systems-approach to NAD+ restoration. Biochem Pharmacol.
-
Myong, S., Nguyen, A., & Challa, S. (2024). NAD+ metabolism in gynecological cancers. Cancers.
-
Li, X., et al. (2022). NNMT as a biomarker and therapeutic target in cancer. Front Oncol.
-
Liu, J., et al. (2021). NNMT in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Biomed Res Int.
















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.