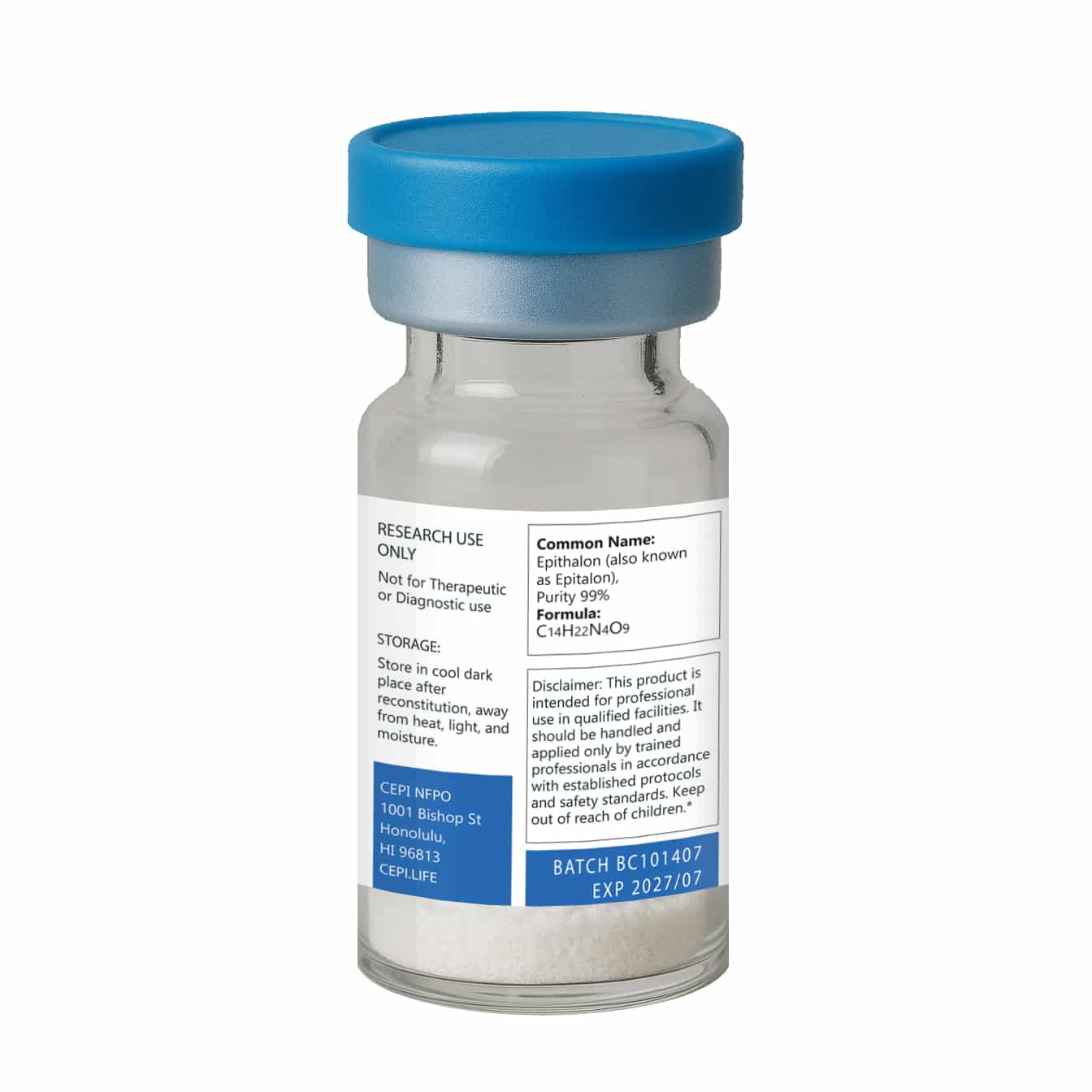
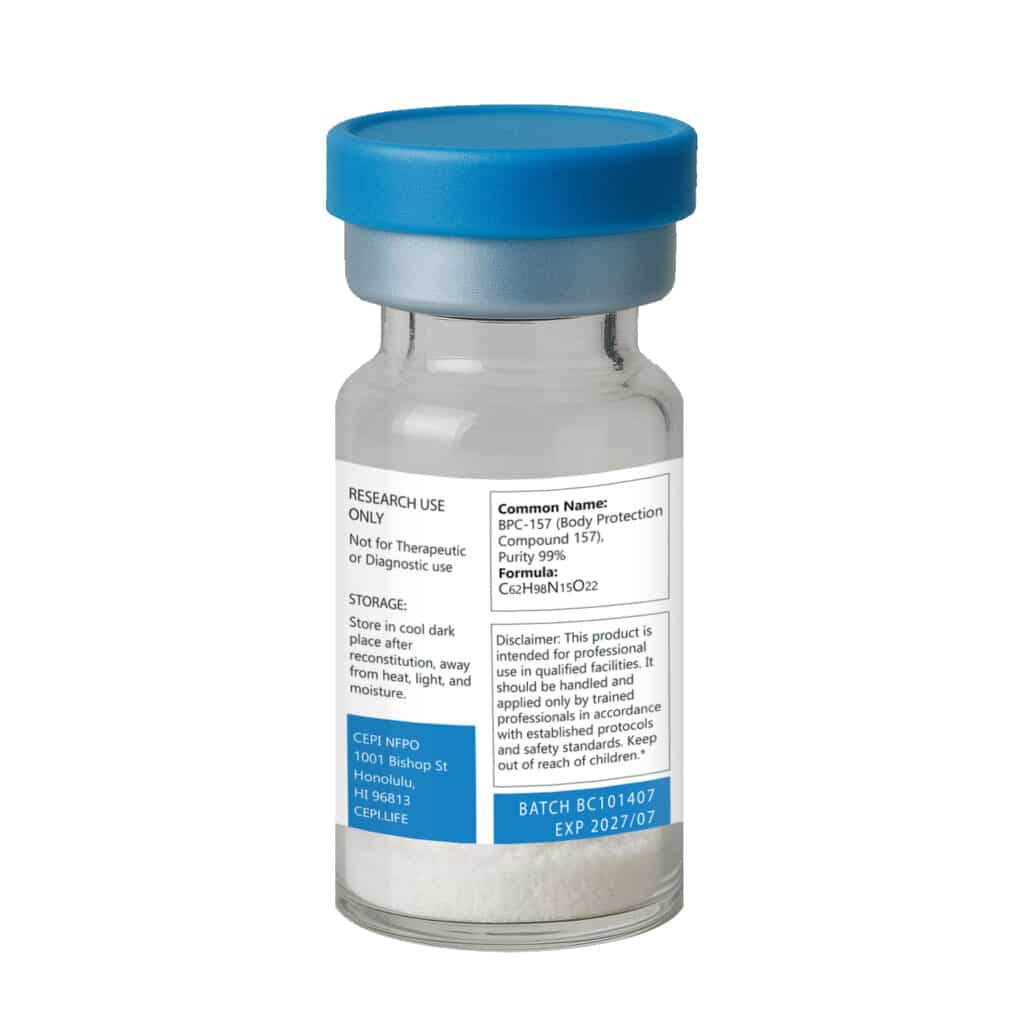
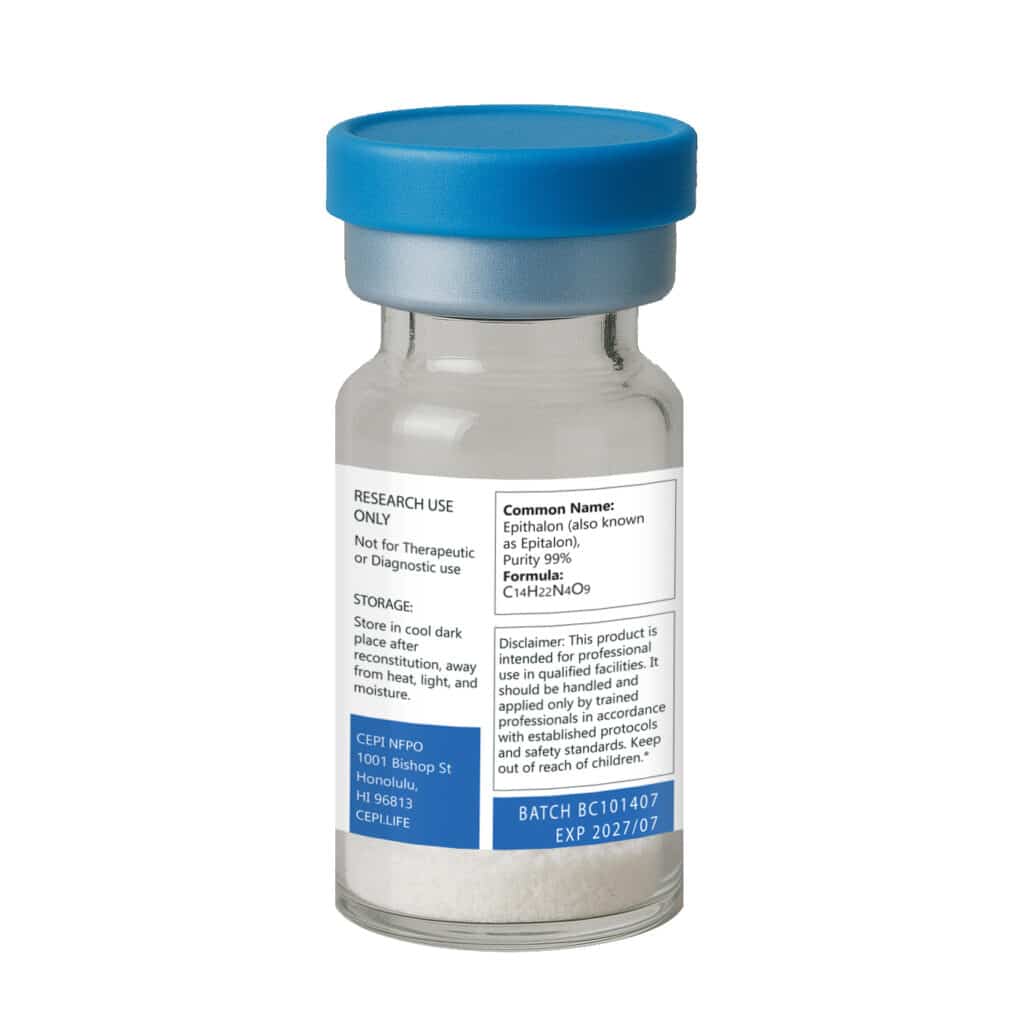
Epithalon 50 mg
Epithalon 50 is a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) developed as an analog of the naturally occurring pineal gland peptide Epithalamin. It has been widely studied for its potential role in regulating cellular health, longevity, and age-associated processes.
$79.99
Key Points
-
Telomere Support: Research indicates Epithalon may stimulate telomerase activity, helping to maintain telomere length—an important factor in cellular aging.
-
Cellular Protection: Shown in preclinical studies to modulate oxidative stress and support DNA repair mechanisms.
-
Circadian Rhythm Regulation: Early investigations suggest potential benefits in normalizing melatonin production and sleep cycles.
-
Immune & Endocrine Balance: May influence pineal, hypothalamic, and pituitary functions involved in hormonal and immune system regulation.
Research Use Only
Epithalon is provided as a 10 mg lyophilized peptide in a sterile vial. This product is intended for laboratory research purposes only. It is not a drug, food, or dietary supplement, and is not approved for human consumption.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Epithalon (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) has been studied for its potential role in healthy aging and cellular protection. Research suggests it may:
-
Support telomere maintenance through telomerase activation.
-
Reduce oxidative stress and promote DNA repair.
-
Influence pineal function and circadian rhythm regulation.
-
Contribute to improved immune and endocrine balance.
These findings come from decades of research in Russia, Europe, and more recent international studies.
References
-
Anisimov, V. N., Khavinson, V. K., & Morozov, V. G. (2000). Effects of synthetic tetrapeptide Epitalon on biomarkers of aging, survival, and spontaneous tumor incidence in mice. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, 120(1–3), 45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0047-6374(00)00165-3
-
Khavinson, V. K., & Morozov, V. G. (2003). Peptide regulation of aging: The epitalon experience. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1019(1), 391–396. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1297.071
-
Khavinson, V. K., Linkova, N. S., Dyatlova, A. O., & Kuznik, B. I. (2020). Peptide geroprotectors: Epitalon. Biogerontology, 21(5), 475–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-020-09887-5
-
Bondarev, I. E., Khavinson, V. K., & Butyugov, A. A. (2004). Epitalon increases lifespan of fruit flies. Neuroendocrinology Letters, 25(3), 201–204. PMID: 15361865














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.