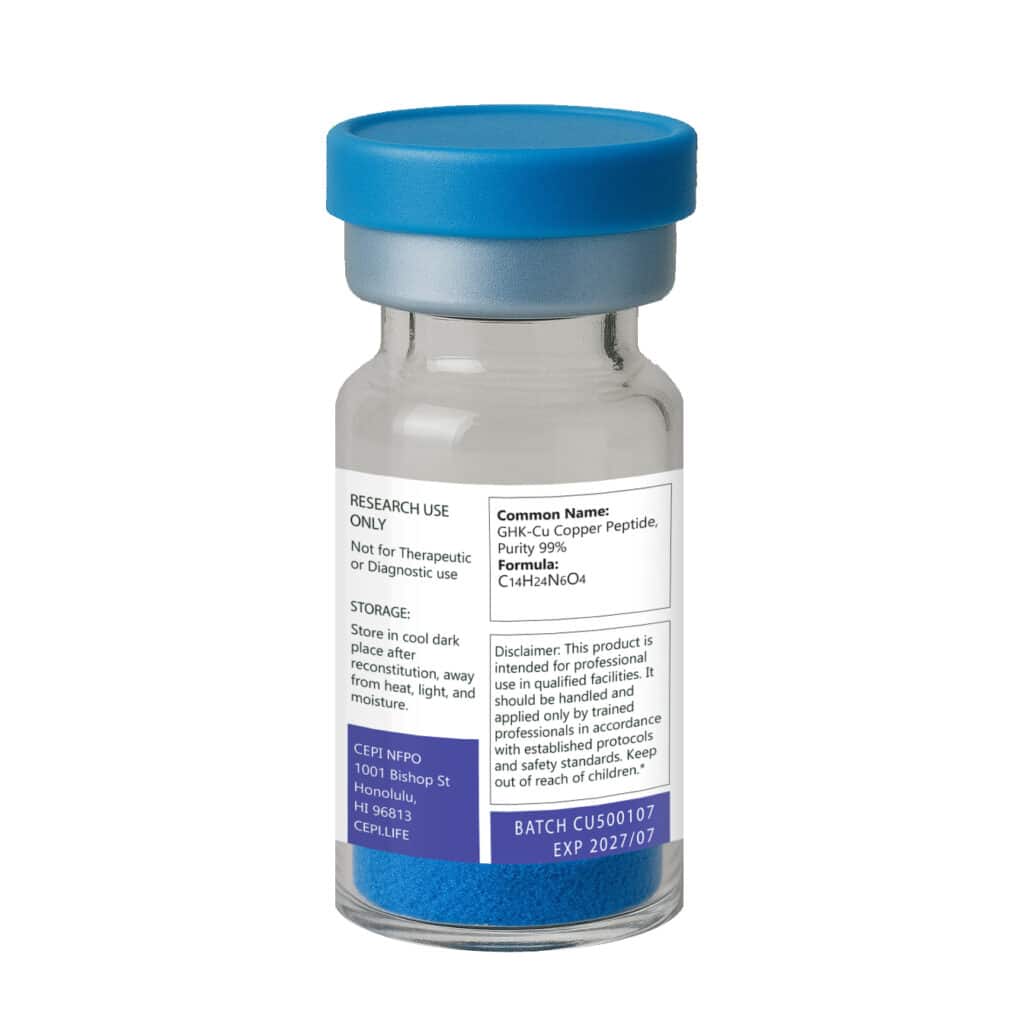
GHK-CU 50 mg
GHK-Cu (Glycyl-L-Histidyl-L-Lysine-Copper) is a naturally occurring copper-binding tripeptide first identified in human plasma and later found in saliva and urine. This short peptide is recognized for its broad regenerative and protective properties, playing a critical role in skin repair, hair growth stimulation, and cellular rejuvenation.
$70.99
Mechanism of Action
GHK-Cu functions primarily as a signaling peptide. By binding copper ions, it activates pathways involved in:
-
Collagen & Elastin Production – Promotes extracellular matrix remodeling and skin firmness.
-
Wound Healing & Tissue Repair – Accelerates angiogenesis and fibroblast activity.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Action – Modulates pro-inflammatory cytokines, reducing oxidative stress.
-
Hair Follicle Stimulation – Encourages follicular cell proliferation and reduces follicle miniaturization.
-
Gene Expression Reset – In laboratory studies, GHK-Cu has been shown to “reset” gene expression in fibroblasts, restoring a more youthful cellular profile.
Key Research Findings
-
Enhances wound healing and tissue repair across skin, mucosa, and connective tissue.
-
Demonstrated ability to thicken hair shafts and stimulate hair regrowth in both animal and human models.
-
Improves skin elasticity, reduces fine lines, and enhances barrier repair.
-
Exhibits strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, protecting against UV and oxidative stress.
Specifications
-
Form: Lyophilized peptide powder
-
Purity: ≥ 98% (HPLC verified)
-
Quantity: 50mg vial
-
Storage: Store dry at -20°C. Reconstituted solutions should be refrigerated (2–8°C).
Intended Use
For laboratory research use only. Not for human consumption, medical, or veterinary use.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
GHK-Cu (Glycyl-L-Histidyl-L-Lysine-Copper) has been extensively studied for its role in tissue repair, skin rejuvenation, and cellular signaling. Below is a summary of key research findings supported by published literature.
Skin & Wound Healing
-
GHK-Cu accelerates wound closure, promotes angiogenesis, and stimulates collagen synthesis. It has been shown to improve healing across skin, connective tissue, and mucosa.【1】
-
It enhances fibroblast proliferation and migration, contributing to more efficient tissue repair.【2】
Anti-Aging & Gene Expression
-
Laboratory studies demonstrate that GHK-Cu can “reset” gene expression in fibroblasts to a more youthful state, reversing age-associated transcriptional changes.【3】
-
It boosts production of collagen, elastin, and glycosaminoglycans, improving skin elasticity and reducing fine lines.【4】
Hair Growth & Follicle Stimulation
-
GHK-Cu promotes hair follicle size enlargement, increases hair shaft thickness, and stimulates regrowth in both animal models and human studies.【5】
Anti-Inflammatory & Protective Effects
-
The peptide modulates pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduces oxidative stress, protecting cells from free radical and UV-induced damage.【6】
-
It exhibits antioxidant activity through copper ion transport and regulation of superoxide dismutase (SOD).【7】
References
-
Pickart, L., & Thaler, M. M. (1973). Tripeptide in human serum that prolongs survival of normal liver cells and stimulates growth in neoplastic liver. Nature New Biology, 243(124), 85–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/newbio243085a0
-
Maquart, F. X., Pickart, L., Laurent, M., Gillery, P., Monboisse, J. C., & Borel, J. P. (1988). Stimulation of collagen synthesis in fibroblast cultures by the tripeptide-copper complex GHK-Cu. FEBS Letters, 238(2), 343–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(88)80472-8
-
Campbell, J., & Pickart, L. (2007). GHK peptide as a natural modulator of multiple cellular pathways in skin regeneration. Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition, 18(12), 1435–1449. https://doi.org/10.1163/156856207782177963
-
Siméon, A., Emonard, H., Hornebeck, W., & Maquart, F. X. (2000). The tripeptide–copper complex glycyl-histidyl-lysine-Cu²⁺ stimulates matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression by fibroblast cultures. Life Sciences, 67(18), 2257–2265. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-3205(00)00805-0
-
Houchi, H., & Oshima, Y. (1993). Hair growth promotion by GHK-Cu in human hair follicle organ culture. Archives of Dermatological Research, 285(8), 449–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00371848
-
Pickart, L., Vasquez-Soltero, J. M., & Margolina, A. (2015). GHK peptide as a natural modulator of multiple cellular pathways in skin regeneration. BioMed Research International, 2015, 648108. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/648108
-
Pickart, L., Margolina, A., & Vasquez-Soltero, J. M. (2012). GHK peptide as a natural modulator of multiple biological pathways. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 34(5), 416–423. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2494.2012.00744.















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.